Yo, diving into the world of Capital gains tax rates, where we break down the nitty-gritty details in a way that’s easy to vibe with. Get ready to level up your knowledge game!
Let’s start by understanding what capital gains tax rates are and how they play a major role in the financial world.
Overview of Capital Gains Tax Rates
When it comes to capital gains tax rates, it’s all about the money you make from selling assets like stocks, real estate, or other investments. These rates determine how much tax you owe on the profit you made from these transactions.
Types of Capital Gains Tax Rates
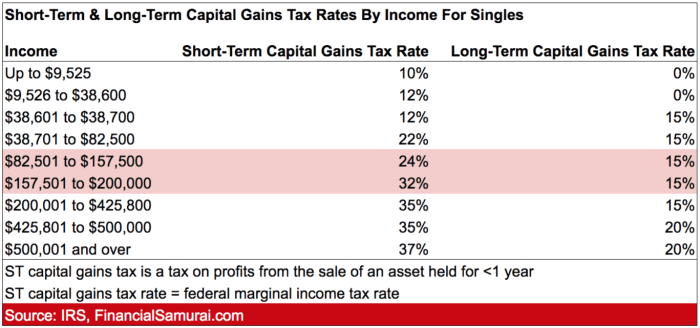
- Short-term Capital Gains Tax Rate: This rate applies to assets held for one year or less before selling. The tax is calculated based on your regular income tax rate, which can range from 10% to 37%.
- Long-term Capital Gains Tax Rate: Assets held for more than one year fall under this rate. The tax rate is usually lower than the short-term rate, ranging from 0% to 20% depending on your income level.
Remember, the longer you hold onto an asset, the lower your tax rate will likely be.
Calculating Capital Gains Tax Rates
- To calculate your capital gains tax, subtract the purchase price of the asset from the selling price to determine your profit.
- Next, apply the appropriate tax rate based on whether it’s a short-term or long-term gain.
- Finally, include any adjustments or deductions that may apply to reduce your taxable gain.
Impact of Capital Gains Tax Rates
When it comes to capital gains tax rates, changes in these rates can have a significant impact on investors and the overall economy. Let’s dive into how varying tax rates influence investment decisions and compare the effects of high versus low capital gains tax rates.
Effect on Investors
- Changes in capital gains tax rates can impact the decisions of investors regarding when to buy or sell assets. Higher tax rates may discourage selling investments, leading to longer holding periods.
- Lower tax rates, on the other hand, may incentivize investors to sell assets more frequently to take advantage of favorable tax treatment.
- Investors also consider after-tax returns when making investment decisions, so changes in capital gains tax rates can affect the overall profitability of their investments.
Impact on Investment Decisions
- High capital gains tax rates can discourage investment in the stock market and other assets, potentially slowing down economic growth.
- Conversely, lower capital gains tax rates may stimulate investment activity, leading to increased capital formation and economic development.
- Investors may also shift their focus towards tax-favored investments in response to changes in capital gains tax rates.
Historical Trends in Capital Gains Tax Rates
In understanding the landscape of capital gains tax rates, it is crucial to delve into the historical trends that have shaped these tax rates over the years.
Analysis of Historical Changes
- Historically, capital gains tax rates in the United States have fluctuated significantly, with changes occurring due to shifts in economic policies, political agendas, and overall tax reform efforts.
- For example, in the 1980s, under President Reagan, capital gains tax rates were reduced to stimulate investment and economic growth.
- Conversely, in the early 1990s, capital gains tax rates were increased as part of deficit reduction measures.
Reasons Behind Fluctuations
- The fluctuations in capital gains tax rates are often driven by the government’s goals to either incentivize investment or generate revenue for public spending.
- Political ideologies and economic conditions play a significant role in determining whether capital gains tax rates are raised or lowered.
- Changes in administration and legislative priorities also influence the direction of capital gains tax rates over time.
Evolution of Capital Gains Tax Rates
- Over the years, a pattern has emerged where capital gains tax rates tend to be adjusted in response to economic conditions, such as recessions or periods of economic growth.
- There is a continual debate on the optimal level of capital gains tax rates to strike a balance between encouraging investment and ensuring tax fairness.
- Technological advancements, globalization, and financial market developments have also impacted the evolution of capital gains tax rates in the modern era.
International Comparison of Capital Gains Tax Rates
When it comes to comparing capital gains tax rates across different countries, it’s important to understand how these variations can impact global investment trends. Investors often look at the tax implications before deciding where to invest their money.
High Capital Gains Tax Rates
- In Denmark, the capital gains tax rate can go as high as 42%, making it one of the highest in the world.
- Similarly, in France, the capital gains tax rate can reach up to 30%, which can deter investors from realizing gains.
Low Capital Gains Tax Rates
- On the other hand, countries like Singapore and Switzerland have relatively low capital gains tax rates, at 0% and 15% respectively.
- These lower tax rates can attract more investors looking to maximize their returns on investments.
Impact on Global Investment Trends
The differences in capital gains tax rates play a significant role in shaping global investment trends. Countries with lower tax rates tend to attract more foreign investments, leading to economic growth and development. On the other hand, high tax rates can discourage investors and lead to capital flight.
