When it comes to borrowing money, your credit score plays a crucial role in determining your loan options and terms. From interest rates to loan approval decisions, understanding how credit scores impact loans is essential for financial success. Let’s dive into the world of credit scores and loans to uncover the mysteries behind this important financial factor.
Understanding Credit Scores
Credit scores are numerical representations of an individual’s creditworthiness, indicating the likelihood of repaying debts. These scores are calculated based on various factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit used, and new credit accounts.
Factors Influencing Credit Scores
- Payment History: Timely payments positively impact credit scores.
- Credit Utilization: Keeping credit card balances low relative to credit limits is crucial.
- Length of Credit History: Longer credit history shows responsible credit management.
- Types of Credit Used: A mix of credit types, like credit cards and loans, can be beneficial.
- New Credit Accounts: Opening multiple accounts in a short time can lower credit scores.
Importance of Credit Scores in Loan Approval
Credit scores play a significant role in the loan approval process as lenders use them to assess the risk associated with lending money. Higher credit scores indicate lower risk, making borrowers more attractive for loans with favorable terms and interest rates. On the other hand, lower credit scores can result in higher interest rates or even denial of loan applications.
Impact of Credit Scores on Loan Approval
Having a good credit score is crucial when it comes to getting approved for a loan. Lenders use your credit score to evaluate your creditworthiness and determine the terms of the loan they can offer you. Here’s how credit scores affect loan approval decisions:
Credit Score Ranges and Loan Terms
- Excellent Credit (above 800): Borrowers with excellent credit scores are likely to get approved for loans easily and receive the best terms, such as lower interest rates and higher loan amounts.
- Good Credit (700-799): Individuals with good credit scores may also qualify for loans with favorable terms, but they might not get the absolute best rates available.
- Fair Credit (600-699): Borrowers with fair credit scores may still be approved for loans, but they may face higher interest rates and stricter terms compared to those with higher scores.
- Poor Credit (below 600): People with poor credit scores may struggle to get approved for loans, and if they do, they are likely to face very high interest rates and unfavorable terms.
Relationship Between Credit Scores and Interest Rates
Lenders use credit scores as a key factor in determining the interest rate they offer on a loan. The higher your credit score, the lower the interest rate you are likely to receive. On the other hand, a lower credit score can result in higher interest rates, as lenders see borrowers with lower scores as higher risk.
Remember, maintaining a good credit score is essential for not only getting approved for loans but also for securing the best possible terms and interest rates. Your credit score truly matters when it comes to borrowing money.
Credit Score Requirements for Different Types of Loans
When it comes to applying for different types of loans, credit score requirements can vary significantly. Lenders use credit scores to assess the risk of lending money to borrowers, and different types of loans come with different risk levels.
Mortgage Loans
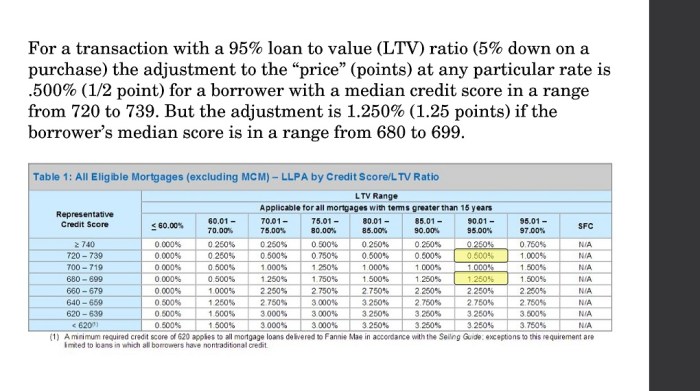
For mortgage loans, which involve a large amount of money and a long repayment period, lenders typically require a higher credit score compared to other types of loans. A credit score of 620 or higher is usually needed to qualify for a conventional mortgage, while FHA loans may accept credit scores as low as 500 with a larger down payment.
Auto Loans
Auto loans, on the other hand, may have more lenient credit score requirements as the car itself serves as collateral for the loan. While a credit score of 660 or higher is considered good for auto loans, some lenders may offer financing options to borrowers with credit scores as low as 500, albeit with higher interest rates.
Personal Loans
Personal loans, which are unsecured loans not backed by collateral, often have higher credit score requirements compared to auto loans but lower than mortgage loans. Lenders typically look for a credit score of 580 or higher to qualify for a personal loan, although some online lenders may offer loans to borrowers with scores as low as 500.
Strategies to Improve Credit Scores for Better Loan Terms
Improving your credit score is crucial for securing better loan terms and financial opportunities. By taking proactive steps to boost your creditworthiness, you can access lower interest rates, higher loan amounts, and more favorable repayment terms. Here are some actionable strategies to enhance your credit score and maximize your borrowing potential:
1. Pay Your Bills on Time
One of the most effective ways to improve your credit score is to consistently pay your bills on time. Late payments can have a significant negative impact on your credit rating, so make sure to stay current with all your financial obligations.
2. Reduce Your Credit Utilization Ratio
Your credit utilization ratio is the amount of credit you are using compared to the total credit available to you. Aim to keep this ratio below 30% to demonstrate responsible credit management and boost your credit score.
3. Check Your Credit Report Regularly
Monitor your credit report regularly to identify any errors or discrepancies that could be dragging down your credit score. By addressing inaccuracies promptly, you can ensure that your credit profile is an accurate reflection of your financial behavior.
4. Avoid Opening Too Many New Accounts
Opening multiple new credit accounts within a short period can signal financial distress to lenders and lower your credit score. Be strategic about applying for new credit and only open accounts when necessary.
5. Maintain a Mix of Credit Types
Diversifying the types of credit accounts you have, such as credit cards, installment loans, and mortgages, can demonstrate your ability to manage various forms of credit responsibly. This can positively impact your credit score over time.
6. Keep Older Accounts Open
The length of your credit history plays a role in determining your credit score. Keep older accounts open, even if you no longer use them, to maintain a longer credit history and potentially improve your credit score.
