Kicking off with Asset allocation strategies, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone american high school hip style that unfolds with each word.
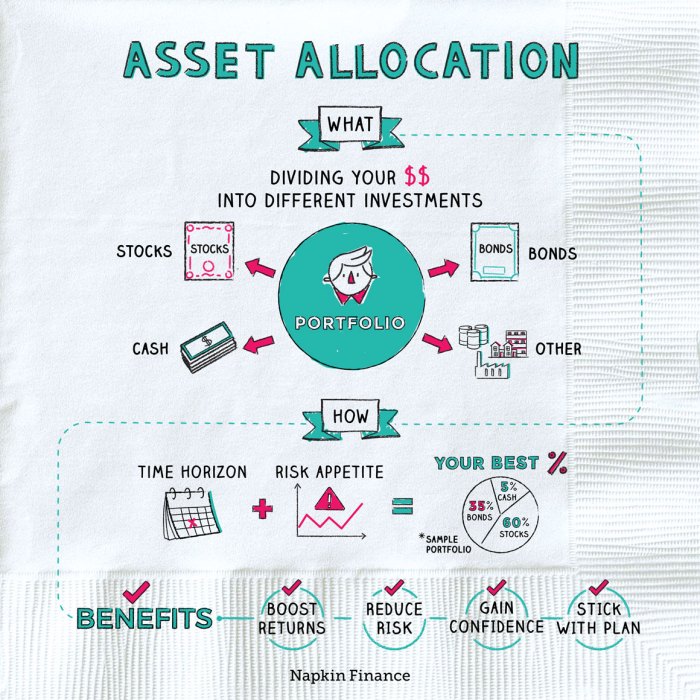
When it comes to making your money work for you, understanding asset allocation strategies is key. By diversifying your investments across different types of assets, you can maximize returns and minimize risks. Let’s dive into the world of asset allocation and explore the various strategies that can help you achieve your financial goals.
Types of Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation strategies are crucial in managing investment portfolios effectively. Different types of asset allocation strategies are utilized by investors to achieve various financial goals and manage risk. Let’s explore some common strategies:
1. Strategic Asset Allocation, Asset allocation strategies
Strategic asset allocation involves setting target allocations for various asset classes based on a long-term investment horizon and risk tolerance. The primary objective is to create a well-diversified portfolio that aligns with the investor’s financial goals.
- Characteristics: Long-term focus, predetermined asset allocation percentages, periodic rebalancing.
- Objectives: Achieve a balance between risk and return, maintain consistent exposure to asset classes.
- Risk-Return Profile: Moderate risk, stable returns over the long term.
2. Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments to the portfolio based on market conditions or economic outlook. The goal is to capitalize on short-term opportunities or manage risks efficiently.
- Characteristics: Dynamic allocation based on market trends, active management approach.
- Objectives: Enhance returns by exploiting short-term market inefficiencies, manage downside risk.
- Risk-Return Profile: Higher risk due to active trading, potential for higher returns if market timing is successful.
3. Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation combines elements of both strategic and tactical approaches. It involves adjusting the asset allocation based on a predefined set of rules or triggers, such as valuation metrics or economic indicators.
- Characteristics: Rules-based approach, automated adjustments based on specific criteria.
- Objectives: Capture opportunities in changing market conditions, reduce downside risk through systematic adjustments.
- Risk-Return Profile: Depends on the effectiveness of the rules-based system, potential for enhanced returns with lower risk.
Importance of Asset Allocation
When it comes to building a solid investment portfolio, asset allocation is key. It involves spreading your investments across different asset classes like stocks, bonds, and cash to help manage risk and optimize returns. Let’s dive into why asset allocation is crucial for your financial success.
Managing Risk with Asset Allocation
Asset allocation plays a crucial role in managing risk in your investment portfolio. By diversifying your investments across various asset classes, you can reduce the impact of market volatility on your overall portfolio. For example, if you have all your money invested in stocks and the stock market takes a hit, your portfolio will suffer major losses. However, if you have a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash, the impact of a stock market downturn can be minimized.
This way, you can protect your investments from significant losses and ensure a more stable financial future.
Impact on Portfolio Performance
Asset allocation also has a direct impact on your portfolio’s performance. By strategically allocating your assets based on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon, you can potentially enhance your returns while minimizing risks. For instance, if you are a young investor with a long time horizon, you may choose to allocate a higher percentage of your portfolio to stocks for greater growth potential.
On the other hand, if you are nearing retirement, you may shift towards a more conservative asset allocation to protect your wealth.
Factors Influencing Asset Allocation
When it comes to choosing asset allocation strategies, several key factors come into play. Factors such as age, risk tolerance, financial goals, and economic conditions all play a crucial role in determining the most suitable asset allocation mix for an individual or organization.
Age
Age is a significant factor that influences asset allocation decisions. Younger individuals may opt for a more aggressive allocation with a higher percentage of stocks, seeking higher returns over the long term. On the other hand, older individuals nearing retirement may prefer a more conservative approach with a higher allocation to bonds and cash for capital preservation.
Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance refers to an individual’s ability and willingness to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments. Those with a higher risk tolerance may choose a more aggressive allocation with a higher percentage of stocks, while those with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative approach with a higher allocation to bonds and other fixed-income securities.
Financial Goals
Financial goals, such as saving for retirement, education, or purchasing a home, also influence asset allocation decisions. Different goals may require different investment strategies, with varying levels of risk and return potential. It is essential to align asset allocation with specific financial objectives to achieve desired outcomes.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions, such as inflation, interest rates, and market trends, can impact asset allocation choices. In times of high inflation, investors may seek assets that provide protection against rising prices, such as commodities or real estate. During periods of low-interest rates, investors may favor equities for higher potential returns.
Asset Classes in Asset Allocation: Asset Allocation Strategies
In asset allocation, different asset classes are used to build a diversified portfolio. Each asset class has its own characteristics and risk profile, allowing investors to spread out their investments and minimize overall risk.
Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company and offer potential for high returns but come with high volatility. They are considered high-risk, high-reward investments. Examples include Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They provide a fixed income stream and are generally considered lower risk compared to stocks. Examples include US Treasury bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds.
Real Estate
Real estate involves investing in properties such as residential homes, commercial buildings, and land. It offers potential for appreciation and rental income but can be illiquid and requires ongoing maintenance.
Commodities
Commodities are raw materials or primary agricultural products that can be bought and sold, such as gold, oil, and wheat. They can provide a hedge against inflation and geopolitical risks but are highly volatile.Diversifying across these asset classes can optimize portfolio performance by reducing overall risk. By spreading investments across different types of assets, investors can benefit from the strengths of each asset class while minimizing the impact of any single asset’s downturn.
