Yo, peeps! Ready to dive into the world of retirement fund allocation? Get ready to learn all about how to make that money work for you in the long run. From classic strategies to modern twists, we’re about to break it down for you in a way that’s as cool as your favorite jam.
Now, let’s break it down and see what’s good with retirement fund allocation.
Fundamentals of Retirement Fund Allocation
Retirement fund allocation is the process of dividing your investment portfolio among different asset classes to achieve a balance between risk and return that aligns with your retirement goals. It is crucial to allocate funds strategically to ensure long-term financial security during retirement.
Asset Classes Suitable for Retirement Fund Allocation
- Stocks: Investing in stocks can provide high returns over the long term but comes with higher risk due to market volatility. It is essential to diversify your stock holdings to reduce risk.
- Bonds: Bonds offer a more stable source of income compared to stocks, making them a suitable choice for conservative investors looking for steady cash flow.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments can provide both rental income and potential appreciation in property value, offering a hedge against inflation.
Key Factors to Consider in Fund Allocation
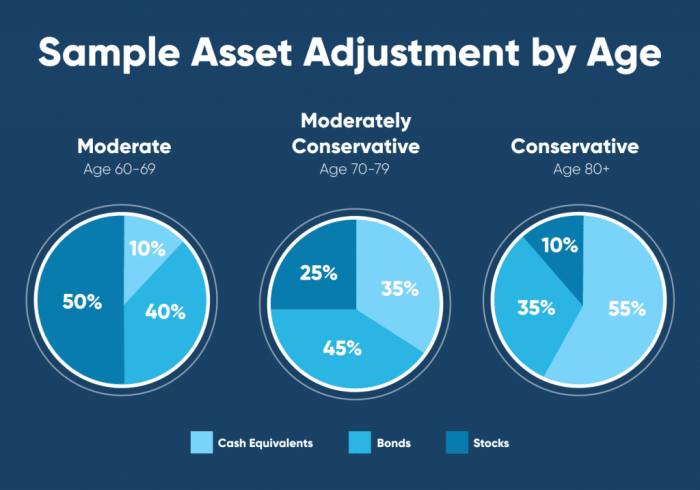
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your risk tolerance to determine the mix of investments that align with your comfort level. Younger investors can typically afford to take on more risk, while those nearing retirement may opt for a more conservative approach.
- Time Horizon: Consider the time remaining until your retirement when allocating funds. Long-term investors can afford to take more risks, while those close to retirement may prioritize capital preservation.
- Diversification: Diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes can help reduce risk and protect against market downturns. Avoid putting all your eggs in one basket.
Traditional vs. Modern Approaches
In the realm of retirement fund allocation, there are distinct differences between traditional and modern approaches. Let’s delve into the comparison and contrast between these two strategies.
Traditional Methods of Retirement Fund Allocation
In the past, traditional methods of retirement fund allocation often involved a conservative approach, focusing on low-risk investments such as bonds and savings accounts. These methods prioritized capital preservation over high returns, resulting in slower wealth accumulation over time.
Modern Strategies for Retirement Fund Allocation
On the other hand, modern approaches to retirement fund allocation embrace a more dynamic and diversified portfolio. With advancements in technology and financial tools, investors now have access to a wide range of investment options such as index funds, ETFs, and robo-advisors. These modern strategies aim to optimize returns while managing risks effectively.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have revolutionized retirement fund allocation practices by providing investors with real-time data, automated investment tools, and personalized financial advice. Robo-advisors, for example, use algorithms to create and manage portfolios based on individual risk tolerance and financial goals, making investing more accessible and efficient.
Examples of Traditional and Modern Investment Vehicles
– Traditional: Certificates of Deposit (CDs) and Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are examples of traditional investment vehicles used for retirement fund allocation. These instruments offer fixed returns and tax advantages, albeit with limited growth potential.
– Modern: Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and target-date funds are popular modern investment vehicles for retirement fund allocation. ETFs provide diversification and low-cost exposure to various asset classes, while target-date funds automatically adjust asset allocation based on the investor’s age and retirement timeline.
Risk Management in Retirement Fund Allocation
When it comes to managing risk in retirement fund allocation, there are several strategies that can be employed to ensure a more secure financial future. One of the key ways to mitigate risk is through proper diversification of your investment portfolio. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce the impact of any one investment performing poorly. Additionally, adjusting asset allocation based on your risk tolerance and time horizon is crucial in ensuring that you are comfortable with the level of risk you are taking on and that your investments align with your retirement goals.
Diversification in Retirement Portfolios
Diversification is a fundamental strategy in managing risk in retirement fund allocation. By investing in a mix of asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, you can reduce the overall risk in your portfolio. This is because different asset classes tend to perform differently under various market conditions. For example, when stocks are performing poorly, bonds or real estate investments may provide stability and help offset losses. It is important to regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure that your asset allocation remains diversified and aligned with your risk tolerance.
Adjusting Asset Allocation
Adjusting asset allocation based on your risk tolerance and time horizon is essential in managing risk in retirement fund allocation. Your risk tolerance refers to your willingness and ability to withstand fluctuations in the value of your investments. If you have a low risk tolerance, you may opt for a more conservative investment approach with a higher allocation to bonds and cash. On the other hand, if you have a higher risk tolerance and a longer time horizon, you may be comfortable with a more aggressive investment strategy with a higher allocation to stocks. It is important to regularly reassess your risk tolerance and adjust your asset allocation accordingly to ensure that your investment strategy remains aligned with your retirement goals.
Tax Considerations and Retirement Fund Allocation
When it comes to planning for retirement, understanding the tax implications of different retirement accounts is crucial in determining how to allocate your funds effectively.
Tax Implications of Different Retirement Accounts
- 401(k): Contributions to a traditional 401(k) are typically made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income in the current year. However, withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
- IRA: Traditional IRAs offer similar tax advantages to 401(k)s, with contributions being tax-deductible and withdrawals taxed as income. Roth IRAs, on the other hand, are funded with after-tax dollars, allowing for tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
Tax-Efficient Strategies for Retirement Fund Allocation
- Consider maximizing contributions to tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs to lower your current tax liability.
- Utilize tax-loss harvesting to offset capital gains in taxable investment accounts and reduce your overall tax burden.
- Diversify your retirement portfolio with a mix of taxable and tax-advantaged investments to optimize tax efficiency.
Tax-Advantaged Investments for Retirement Portfolios
- Municipal Bonds: Interest earned on municipal bonds is typically exempt from federal taxes, making them a tax-efficient investment for retirement accounts.
- Index Funds: These passively managed funds often have lower turnover, resulting in fewer capital gains distributions and reduced tax implications for investors.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free, making them a valuable tool for retirement healthcare costs.
